การศึกษาคุณสมบัติปอซโซลานของเถ้าถ่านหินบิทูมินัส
Main Article Content
Abstract
Khuanjit Hemavibool, Saranagon Hemavibool and Sairoong Ouypornkochagorn
รับบทความ: 14 ธันวาคม 2560; แก้ไขบทความ: 29 มีนาคม 2561; ยอมรับตีพิมพ์: 11 มิถุนายน 2561
บทคัดย่อ
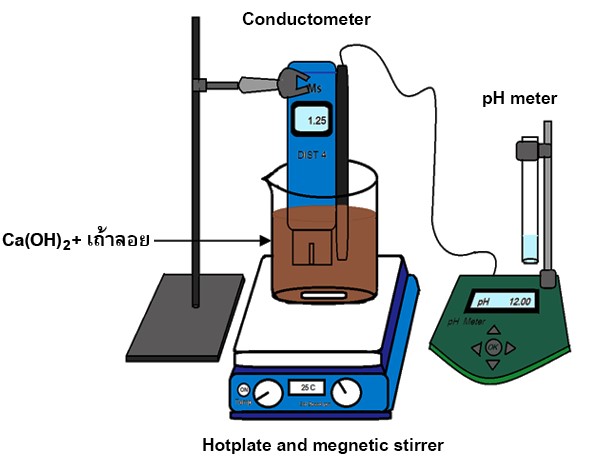
เถ้าถ่านหินหรือเถ้าลอยเป็นวัสดุปอซโซลานที่นิยมนำมาใช้เป็นวัสดุผสมในงานคอนกรีตต่าง ๆ เพื่อทดแทนการใช้ซีเมนต์ การประเมินคุณสมบัติปอซโซลานของเถ้าลอยจึงมีความสำคัญเพิ่มขึ้นในปัจจุบัน เนื่องจากมีความต้องการผลิตภัณฑ์คอนกรีตที่ยั่งยืนมากขึ้น งานวิจัยนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาคุณสมบัติปอซโซลานของเถ้าลอยจากจังหวัดระยองที่ได้จากการเผาไหม้ถ่านหินบิทูมินัสจากสี่แหล่ง คือ Blair Athol (B), Blair Athol Malavan (BM), Hunter Valley (H) และ Hunter Malavan (HM) จากการศึกษาสมบัติทางเคมีและกายภาพพบว่าเถ้าลอยทั้งสี่ชนิดจัดอยู่ในประเภท F และจากการประเมินความสามารถในการทำปฏิกิริยาปอซโซลานิกด้วยการติดตามค่าการนำไฟฟ้าของสารผสมเถ้าลอยในสารละลายแคลเซียมไฮดรอกไซด์ พบว่า มีความไวในการเกิดปฏิกิริยาปอซโซลานิกระดับเดียวกัน ข้อมูลที่ได้จากงานวิจัยนี้ช่วยในการประเมินสมบัติเบื้องต้นของเถ้าลอยที่จะนำไปใช้เป็นวัสดุทดแทนซีเมนต์ ซึ่งสามารถช่วยลดปัญหามลพิษที่เกิดจากการผลิตซีเมนต์และยังช่วยลดปัญหาการกำจัดเถ้าลอย
คำสำคัญ: คุณสมบัติปอซโซลาน เถ้าถ่านหินบิทูมินัส ค่าการนำไฟฟ้า
Abstract
The pulverized fuel ash or fly ash is commonly used as a substitute for cement within concrete in various applications. Assessment of the pozzolanic property of fly ash is increasingly important because of the need for more sustainable cementitious products. The aims of this research is to investigate the pozzolanic property of Rayong fly ashes which are byproduct from burning four types of pulverized Bituminous coals including Blair Athol (B), Blair Athol Malavan (BM), Hunter Valley (H) and Hunter Malavan (HM). These fly ashes were all classified as a Class F by chemical and physical characterizations. Evaluation of pozzolanic activity of fly ashes was carried out by monitoring of conductivity of fly ash suspensions in calcium hydroxide solution, classifying all fly ashes in same reactivity level. The results from this study would help to evaluate the quality of bituminous fly ashes for use as a cement replacement in order to reduce pollution caused by cement production and solve disposal problems of fly ash.
Keywords: Pozzolanic property, Bituminous fly ash, Conductivity
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
ASTM C618 Standard Specification for Coal Fly Ash and Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use in Concrete Published By: ASTM International (ASTM) Published Date: December 15, 2017.
Baert, G., Driessche, I. V., Hoste, S., de Schutter, G., and de Belie, N. (2007) Interaction between the pozzolanic reaction of fly ash and the hydration of cement. In The 12th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement. Montreal, Canada.
Bernal, S. A., Rodríguez, E. D., Mejía de Gu-tiérrez, R., and Provis, J. L. (2015). Performance at high temperature of alkali–activated slag pastes produced with silica fume and rice husk ash based activators. Materials de Construcción 65(318): 1–10.
Bjegovic, D., Stirmer, N., and Serdar, M. (2012). Durability properties of concrete with blended cements. Materials and Corrosion 63 (12): 1087–1096.
Jenjirapanya, S., and Krammart, P. (2016). A study on properties of cementitious material using industrial waste. Journal of Industrial Technology 12(2): 77– 86. (in Thai)
Kongsook, M., Hemavibool, S., Tongaroonsri, S., and Tangtermsirikul, S. (2013). Effect of binders on shrinkage cracking behavior of concrete. RMUTP Research Journal, The 5th Rajamangala University of Technology National Conference (Special Is-sue): 588–598.
Lowe, R. (2012). Pozzolanic Properties of Biomass Fly Ash. Master of Science Thesis (Civil Engineering). USA: Clemson University.
Payá, J., Borrachero, M. V., Monzó, J., Peris-Mora, E., and Amahjour, F. (2001). Enhanced conductivity measurement techniques for evaluation of fly ash pozzolanic activity. Cement and Concrete Research 31: 41–49.
Samad, S., Shah, A. and Limbachiya. M.C. (2017). Strength development characteristics of concrete produced with blended cement using ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBS) under various curing conditions. Sadhana 42(7): 1–11.
Sudhakar, M. R., and Asha, K. (2013). Role of fly ash pozzolanic reactions in controlling fluoride release from phosphogypsum. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 25(8): 999–1005.
Vekariya, M. S., and Pitroda, P. (2013). Bacterial concrete: New era for construction industry. International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology 4(9): 4128–4137.
Zhang, J., Liu, G., Chen, B., Song, D., Qi, J. and Liu, X. (2014). Analysis of CO2 emission for the cement manufacturing with alternative raw materials: A LCA-based framework. Energy Procedia 61: 2541–2545.