การพัฒนาขั้วไฟฟ้าจากการวาดด้วยดินสอบนกระดาษทรายสำหรับหาปริมาณแคดเมียมในน้ำ
Main Article Content
Abstract
Puttiphat Benjapreechaphat, Nuanlaor Ratanawimarnwong, and Preecha Mansalai
รับบทความ: 6 ตุลาคม 2560; ยอมรับตีพิมพ์: 25 ธันวาคม 2560
บทคัดย่อ
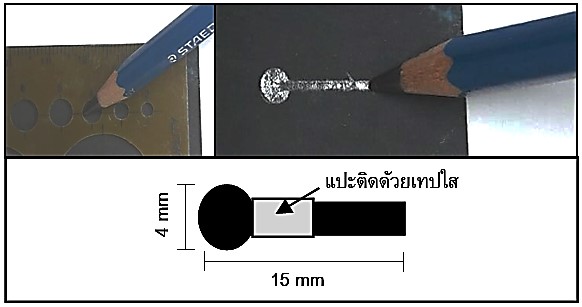
ในงานวิจัยนี้นำเสนอวิธีการที่ง่ายและราคาประหยัดสำหรับการเตรียมอิเล็กโทรเคมิคัลเซนเซอร์ เพื่อใช้ในการวิเคราะห์หาปริมาณแคดเมียมในน้ำ โดยการใช้ขั้วไฟฟ้าแกรไฟต์อย่างง่ายซึ่งผลิตขึ้นจากไส้ดินสอที่ฝนบนกระดาษทราย เมื่อนำขั้วไฟฟ้าแกรไฟต์ที่ผลิตได้มาใช้ร่วมกับเทคนิคสแควร์เวฟอาโนดิกสทริปปิงโวลแทมเมตรี พบว่า มีประสิทธิภาพในการวิเคราะห์หาปริมาณแคดเมียมที่มีปริมาณน้อยได้ จากการศึกษาปัจจัยต่าง ๆ ที่ส่งผลต่อสัญญาณที่ตรวจวัดได้ที่สภาวะที่เหมาะสมให้ช่วงความเป็นเส้นตรงของกราฟมาตรฐานตั้งแต่ 5 µgL-1 ถึง 100 µgL-1 ขีดจำกัดในการตรวจวัดเท่ากับ 0.72 µgL-1 อิเล็กโทรเคมิคัลเซนเซอร์นี้ประสบความสำเร็จในการนำไปประยุกต์ใช้สำหรับการวิเคราะห์แคดเมียมในตัวอย่างน้ำโดยตรง
คำสำคัญ: แคดเมียม ขั้วไฟฟ้าจากการวาดด้วยดินสอ สแควร์เวฟโวลแทมเมตรี
Abstract
This research presented a simple and low-cost approach for electrochemical sensor preparation to determine cadmium in water. The approach employed a simple graphite electrode made of pencil lead via mechanical abrasion onto a sand paper. When using the developed graphite electrode to square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry, the capability for trace analysis of cadmium was observed. Influence of several relevant operating parameters was also investigated. At the optimum condition, linear range of 5 µgL-1 to 100 µgL-1 was provided and detection limit of 0.72 µgL-1 was achieved. The proposed sensor was successfully applied for the direct determination of cadmium in water samples.
Keywords: Cadmium, Pencil drawn electrodes, Square wave voltammetry
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
Alarfaj, N. A., Ammar, R. A., and El-Tohamy, M. F. (2012). Disposable screen-printed sensors for determination of duloxetine hydrochloride. Chemistry Central Journal 6(6): 1–8.
Chawengsri, W. (1994). Cadmium. Toxic Substances News Journal 21(1): 32–36. (in Thai)
Chuanuwatanakul, S., Dungchai, w., Chailapakul, O., and Motomizu, S. (2008). Determination of trace heavy metals by sequential injection–anodic stripping voltam-metry using bismuth film screen-printed carbon electrode. Analytical Sciences 24: 589–594.
Dossi, N., Toniolo, R., Pizzariello, A., Impelliz-zieri, F., Piccin, E., and Bontempelli, G. (2013). Pencil–drawn paper supported electrodes as simple electrochemical detectors for paper–based fluidic devices. Electrophoresis 34: 2085–2091.
Honeychurch, K. C. (2015). The voltammetric behaviour of lead at a hand drawn pencil electrode and its trace determination in water by stripping voltammetry. Analytical Methods 7: 2437–2443.
Matsumoto, A., Osaki, S., Kobata, T., and Hashimoto, B. (2010). Determination of cadmium by an improved double chamber electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spec-trometry. Microchemical Journal 95(1): 85–89.
Pluemphuak, T., Verasan, J., Kamlung, A. and Mala, T. (2015). Cadmium contami-nated in paddy soils and rice yields in Mae Tao and Phra That Pha Daeng Subdistrict, Mae Sot District, Tak Province. Prawaron Agricultural Journal 12(1): 1–8. (in Thai)
Puminat, W. (2004). Cadmium: Hazardous sub-stances of cumulative hazards. Food Journal 34 (4): 298–301. (in Thai)
Rojanarata, T. (2010). Basic of Calculation in Quantitative Analysis. 2nd ed. Nakorn Pathom: Petchkasemkarnpim. (in Thai)
Santhiago, M., Henry, C. S., and Kubota, L. T. (2014). Low cost, simple three dimensional electrochemical paper–based analytical device for determination of p-nitro phenol. Electrochimica Acta 130: 771–777.
Santhiago, M. and Kubota, L. T. (2013). A new approach for paper–based analytical devices with electrochemical detection based on graphite pencil electrodes. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 177: 224–230.
Shankar, R., Groven, L., Amert, A., Whitesb, K. W., and Kellarc J. J. (2011). Non-aqueous synthesis of silver nanoparticles using tin acetate as a reducing agent for the conductive ink formulation in printed electronics. Journal of Materials Chem-istry 21: 10871–10877.
Sriphong, L. (2000). Electrochemical Analysis. Nakorn Pathom: Silpakorn University. (in Thai)