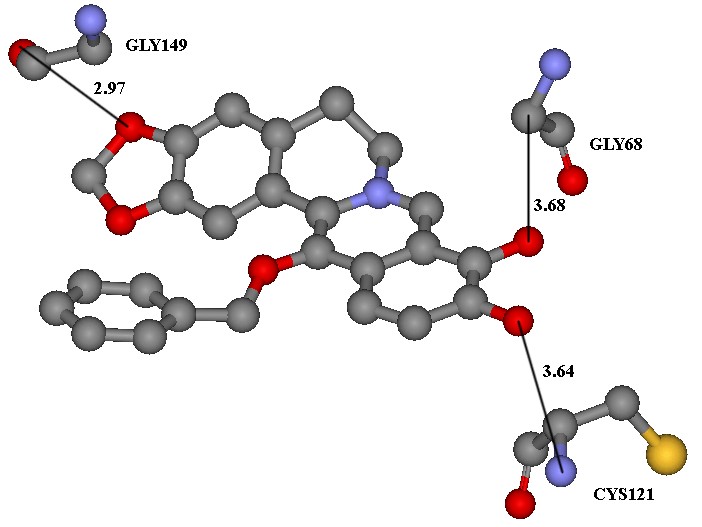
การศึกษาโมเลกุลลาร์ด็อกกิ้งของควิโนนรีดักเตส 2 เป็นเอนไซม์เป้าหมายสำหรับยับยั้งมะเร็งเต้านม
Main Article Content
Abstract
Punnarai Siyapong, Siritron Samosorn and Mayuso Kuno
รับบทความ: 24 ตุลาคม 2556; ยอมรับตีพิมพ์: 12 ธันวาคม 2556
บทคัดย่อ
ควิโนนรีดักเทส 2 (QR2) เป็นเอนไซม์ที่ช่วยเร่งปฏิกิริยารีดักชันของควิโนนไปเป็นไฮโดรควิโนนซึ่งมีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องกระบวนการสังเคราะห์เอสโทรเจน มีรายงานว่าเอนไซม์ QR2 สามารถเร่งปฏิกิริยาการเปลี่ยนควิโนนไปเป็นสารพิษที่มีความว่องไวสูงในการทำลายดีเอ็นเอและมีบทบาทสำคัญในการกระตุ้นให้เกิดมะเร็งเต้านม ดังนั้นการยับยั้งการทำงานของเอนไซม์ QR2 ช่วยป้องกันเซลล์จากการถูกทำลายจากสารพิษเหล่านั้นได้ งานวิจัยนี้ศึกษาโมเลกุลลาร์ด็อกกิ้งของเอนไซม์ QR2 ซึ่งเป็นเอนไซม์เป้าหมายสำหรับยับยั้งการเกิดมะเร็งเต้านม โดยศึกษาโครงสร้างและอันตรกิริยาระหว่างตัวยับยั้ง XM5 กับเอนไซม์ QR2 ที่อยู่ในบริเวณการจับของเอนไซม์ที่มีรหัส 3G5M.pdb จากฐานข้อมูลโครงสร้างของโปรตีน และสารอนุพันธ์ของเบอร์เบอรีนซึ่งมีฤทธิ์ยับยั้งการเจริญ-เติบโตของเซลล์มะเร็งเต้านม MCF–7 โดยใช้วิธีการคำนวณทางโมเลกุลลาร์ด็อกกิ้งด้วยโปรแกรม AutoDock 4.2 เพื่อออกแบบโมเลกุลใหม่หรือพัฒนาโมเลกุลเดิมให้มีประสิทธิภาพในการยับยั้งเอนไซม์ QR2 ดีขึ้น จากการศึกษาพบว่า โครงสร้างของสารอนุพันธ์เบอร์เบอรีนที่มีหมู่แอริลออกซีที่ตำแหน่ง C–13 และมีหมู่ไฮดรอกซิล 2 หมู่ที่ตำแหน่ง C–9 และ C–10 จะให้ค่าพลังงานยึดเหนี่ยวดีที่สุด จากข้อมูลดังกล่าวสามารถออกแบบโครงสร้างตัวยับยั้งที่มีประสิทธิภาพที่ดีขึ้นได้ 3 โครงสร้าง
คำสำคัญ: ควิโนนรีดักเทส 2 โมเลกุลลาร์ด็อกกิ้ง เบอร์เบอรีน มะเร็งเต้านม
Abstract
Quinone reductase 2 (QR2) serves as an enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of quinones to hydroquinones involving in an estrogen synthetic pathway. Recent studies reported that QR2 may transform quinone into highly reactive toxins that are capable of causing more DNA damage and playing a crucial role in stimulating breast cancer. Inhibition of QR2 activities by its inhibitors, therefore, may lead to protection of cells from these toxins. This work focuses on the studies of molecular docking of QR2 inhibitor, XM5, was designed at enzyme binding site coded 3G5M.pdb from structural protein database. Berberine derivatives were designed to show growth inhibiting activity of breast cancer MCF–7. Docking simulation was performed using AutoDock 4.2 to improve the potential to existing QR2 inhibitors. The binding energy calculation using molecular docking showed that the structure of berberine derivatives having an aryloxy group at C–13, and two hydroxyl groups at C–9 and C–10 gave the best result. This finding was accomplished three structures of better potential inhibitors.
Keywords: Quinone reductase 2, Molecular docking, Berberine, Breast cancer
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
ธีรเกียรติ์ เกิดเจริญ. (2539). เคมีคอมพิวเตอร์: คอมพิวเตอร์ช่วยออกแบบโมเลกุลกับการพัฒนานาโนเทคโนโลยี วารสารเทคโนโลยีวัสดุ 39(4): 17–22.
อัญชุลี อุธา. (2554). กินต้านมะเร็งเต้านม. กรุงเทพฯ: บี-เวลล์ สปีเชียล.
Attasara, P., and Buasom, R. (eds). (2011). Hospital-based cancer registry, National Cancer Institute, Department of Medical Services, Ministry of Public Health. (in Thai)
Celli, C.M., Tran, N., Knox, R., and Jaiswal, A. K.. (2006). NRH:quinone oxidoreductase 2 (NQO2) catalyzes metabolic activation of quinones and anti-tumor drugs. Biochemical Pharmacology 72: 366–376.
Foster, C. E., Bianchet, M. A., Talalay, P., Zhao, Q., and Amzel, L. M. (1999). Crystal structure of human quinone reductase type 2, a metalloflavoprotein. Biochemistry 38: 9881–9886.
Frisch, M. J., Trucks, G. W., Schlegel, H. B., Scuseria, G. E., Robb, M. A., Cheeseman, J. R., et al. (2003). Gaussian 03, Revision B05. Pittsburgh, PA: Gaussian.
Ghosh, D., Lo, J., Morton, D., Valette, D., Xi, J., Gris-wold, J., et al. (2012). Novel aromatase inhibitors by structure-guided design. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 55: 8464–8476.
Jamieson, D., Tung, A. T., Knox, R. J., and Boddy, A. V. (2006). Reduction of mitomycin C is catalysed by human recombinant NRH:quinone oxidoreductase 2 using reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide as an electron donating co-factor. British Journal of Cancer 95: 1229–1233.
Knox, R. J., Jenkins, T. C., Hobbs, S. M., Chen, S., Melton, R. G., Burke P. J. (2000). Bioactivation of 5-(aziridin-1-yl)-2,4-dinitrobenzamide (CB 1954) by human NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 2: A novel co-substrate-mediated antitumor prodrug therapy. Cancer Research 60: 4179–4186.
Maiti, A., Reddy, P. V. N., Sturdy, M., Marler, L., Pegan, S. D., Mesecar, A. D., et al. (2009). Synthesis of casimiroin and optimization of its quinone reductase 2 and aromatase inhibitory activities. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 52: 1873–1884.
RCSB PDB Protein Data Bank. (2013). 3G5M. Retrieved from http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=3G5M, March 6, 2013.
Samosorn S. (2011). Thai Petty Patent Application Number 1103000985, 16 September 2011.
Samosorn, S., Tanwirat, B., and Suksamrarn, A. (2011). Thai Patent Application Number 1101002293, 27 September 2011.