การพัฒนาความรู้สึกเชิงจำนวนของเด็กปฐมวัยโดยการจัดประสบการณ์การเล่นแบบชี้แนะ
Main Article Content
Abstract
Jarintra Janthaudomsuk and Oraphan Butkatunyoo
รับบทความ: 12 มิถุนายน 2567; แก้ไขบทความ: 26 กรกฎาคม 2567; ยอมรับตีพิมพ์: 29 กรกฎาคม 2567; ตีพิมพ์ออนไลน์: 7 ธันวาคม 2567
บทคัดย่อ
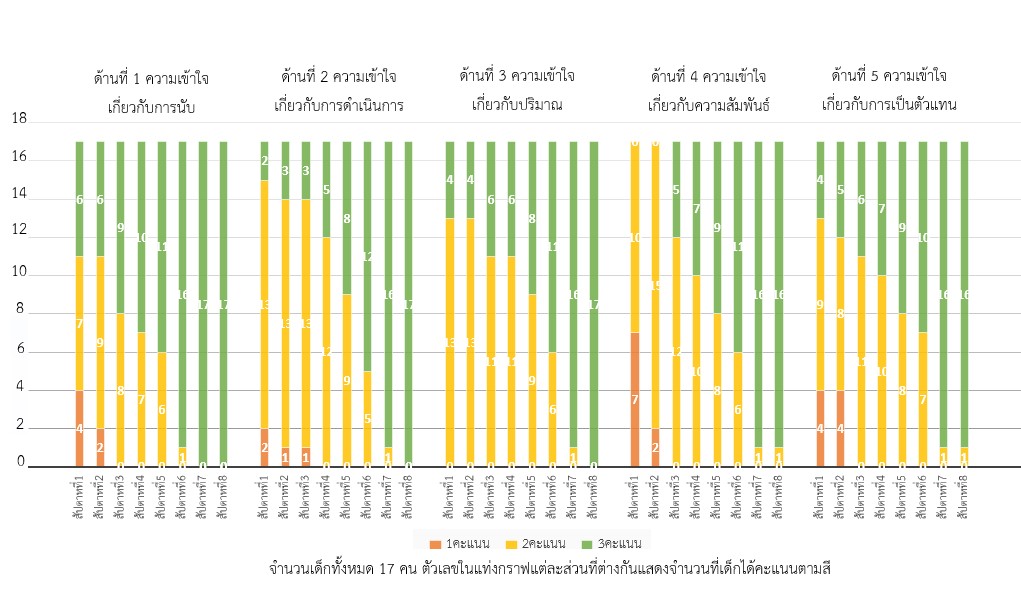
การศึกษาครั้งนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อ 1) ศึกษาผลการจัดประสบการณ์การเล่นแบบชี้แนะเพื่อพัฒนาความรู้สึกเชิงจำนวนของเด็กปฐมวัย 2) ศึกษาพัฒนาการของความรู้สึกเชิงจำนวนของเด็กปฐมวัยที่ได้รับการจัดประสบการณ์การเล่นแบบชี้แนะ กลุ่มเป้าหมาย คือ เด็กปฐมวัย อายุ 5–6 ปี ที่กำลังศึกษาในระดับชั้นอนุบาลปีที่ 3 ภาคเรียนที่ 2 ปีการศึกษา 2566 โรงเรียนสังกัดสำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษาประถมศึกษานนทบุรีเขต 1 จำนวน 17 คน เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการศึกษาประกอบด้วยแผนการจัดประสบการณ์การเล่นแบบชี้แนะเพื่อส่งเสริมความรู้สึกเชิงจำนวน และแบบประเมินความรู้สึกเชิงจำนวนของเด็กปฐมวัย วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลเชิงปริมาณโดยใช้ค่าเฉลี่ย ส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน และวิเคราะห์เชิงคุณภาพโดยวิเคราะห์เนื้อหาและบรรยายเชิงพรรณนา ผลการศึกษา พบว่า 1) การพัฒนาความรู้สึกเชิงจำนวนของเด็กปฐมวัย มีการพัฒนาที่สูงขึ้นทั้งโดยรวมและรายด้าน โดยรายด้านมีการพัฒนาสูงขึ้นตามลำดับ คือ ด้านความเข้าใจเกี่ยวกับการนับ ความเข้าใจเกี่ยวกับการดำเนินการ ความเข้าใจเกี่ยวกับปริมาณ ความเข้าใจเกี่ยวกับการเป็นตัวแทนและความเข้าใจเกี่ยวกับความสัมพันธ์ 2) พัฒนาการของความรู้สึกเชิงจำนวนของเด็กปฐมวัยในภาพรวมตั้งแต่สัปดาห์ที่ 1–8 มีคะแนนเฉลี่ยสูงขึ้นตามลำดับ คือ 1.99 2.11 2.33 2.42 2.53 2.71 2.95 และ 2.98 เด็กมีการพัฒนาความรู้สึกเชิงจำนวน โดยเด็กสามารถนับจำนวน บอกปริมาณ เข้าใจการรวม การแยก ความสัมพันธ์และการเป็นตัวแทนผ่านการทำกิจกรรมคณิตศาสตร์และประยุกต์ใช้ในสถานการณ์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับชีวิตประจำวันได้
คำสำคัญ: ความรู้สึกเชิงจำนวน การจัดประสบการณ์การเล่นแบบชี้แนะ เด็กปฐมวัย พัฒนาการ
Abstract
The objectives of this study were to 1) study the results of providing guided play experiences to develop young children’s number sense, and 2) study the development of young children’s number sense who received guided play experiences. The target group is 17 young children aged 5–6 years who are studying in kindergarten year 3, semester 2, academic year 2023, a school under the Nonthaburi Primary Educational Service Area Office 1. The instruments used in this study consisted of 8 guided play experience lesson plans to promote young children’s number sense and the assessment form of young children’s number sense. Quantitative data were analyzed by using mean and standard deviation, and qualitative data were analyzed by content analysis and descriptive description. The results of this study showed that 1) the development of young children’s number sense was higher both overall and, in each aspect, respectively, in the areas of understanding of counting, operations, quantity, representation and relationships, and 2) development of young children’s number sense in order from 1–8 weeks had higher mean scores at 1.99, 2.11, 2.33, 2.42, 2.53, 2.71, 2.95, 2.98, respectively. Young children can develop their number sense such as counting, quantifying, adding, separation, relationship and representation through doing mathematical activities and applying them in situations related to their daily life.
Keywords: Number sense, Guided play experience provision, Young children, Development
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
Baker, M. J. (2019). Number Sense and the Effects on Students’ Mathematical Success. Retrieved from https://nwcommons.nwciowa.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1160&context=education_masters, July 28, 2023.
Beyond Code Academy. (2023). Come Get to Know the Principles of Learning through Play (Play–Based Learning). Retrieved from https://www.beyondcodeacademy.com/post/play-base-learning-beyondcode, July 28, 2023.
Chaimongkol, C., and Lehmongkol, P. (2021). Effects of loose part activity provision on basic mathematical skills in number sense for young children. Pathumthani University Academic Journal 13(2): 468–484. (in Thai)
Das, B. H., Pasek, H. K., and Golinkoff, R. M. (2017). The Case of Brain Science and Guided Play: A Developing Story. Retrieved from https://templeinfantlab.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2017/12/The-Case-of-Brain-Science-and-Guided-Play-A-Developing-Story.pdf, July 24, 2023.
Gawthorpe, A., and Davidson, C. K. (2023). Active Learners in Numeracy: Implementing Guided Play for Early Numeracy Learning. Retrieved from https:// uel.ac.uk/sites/default/files/rite-june-23-gawthorpe-article-pp-13-20.pdf, May 24, 2023.
Government of Western Australia. (2018). Importance of Play–Based Learning. Retrieved from https://www.education.wa.edu.au/dl/7lpml0, July 28, 2023.
Maghfirah, M., and Mahmudi, A. (2018). Number Sense: The Result of Mathematical Experience. Retrieved from https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/1097/1/012141/pdf, May 24, 2023.
Ministry of Education of Canada. (2016). The “Big Ideas” in number sense and numeration. A Guide to Effective Instruction in Mathematics Kindergarten to Grade 3 Number Sense and Numeration (pp.1–59). Ontario: Queen’s Printer for Ontario.
Nonthaburi Primary Educational Service Area Office 1. (2022). Results of the Ordinary National Educational Test. Retrieved from https://bigdata.nbi1.go.th/tableOnet.php?op=5.1, May 30, 2023.
Reshma, A. (2022, June 7). What is the Importance of Number Sense in Math? Retrieved from https://www.byjusfutureschool.com/blog/what-is-the-importance-of-number-sense-in-math, July 28, 2023.
Stramel, J. (2021). Early Number Concepts and Number Sense. Retrieved from https://fhsu.pressbooks.pub/ecumath/chapter/chapter-9-early-number-concepts-number-sense, May 30, 2023.
Thai Public Broadcasting Service. (2023). PISA Test Results for Thai Children, Lowest Scores in 20 Years, Ministry of Education Sets up Working Group to Fix. Retrieved from https://www.thaipbs.or.th/ news/content/334652, May 30, 2023 (in Thai)
The Institute for the Promotion of Teaching Science and Technology. (2020). The nature of mathematics and the goals for learning mathematics. Framework and Guidelines to Integrated Science, Technology and Mathematics in Early Childhood based on Early Childhood, Curriculum B.E. 2017 (p.50). Bangkok: Gogoprint Thailand. (in Thai)
Toub, T. S., Rajan, V., Golinkoff R. M., and Pasek, K. (2016). Guided Play: A Solution to the Play Versus Learning Dichotomy. Retrieved from https://temple infantlab.com/wpcontent/uploads/sites/2/2017/12/Playful-Learning-A-solution-to-the-play-versus-learning-dichotomy.pdf, May 30, 2023.
University of New Hampshire. (2023). Guided Play in Action. Retrieved from https://chhs.unh.edu/early-childhood/play-based-learning-coaching-teaching/play-based-learning-defined/guided-play-action, May 30, 2023.