In Silico Investigation of Estrogen Receptor Alpha Inhibition by Alkyleneoxyberberine Derivatives
Keywords:
ER-alpha, Berberine, Molecular Dynamic, Molecular Docking, Molecular Mechanics/Generalized Born Surface Area (MM-GBSA)Abstract
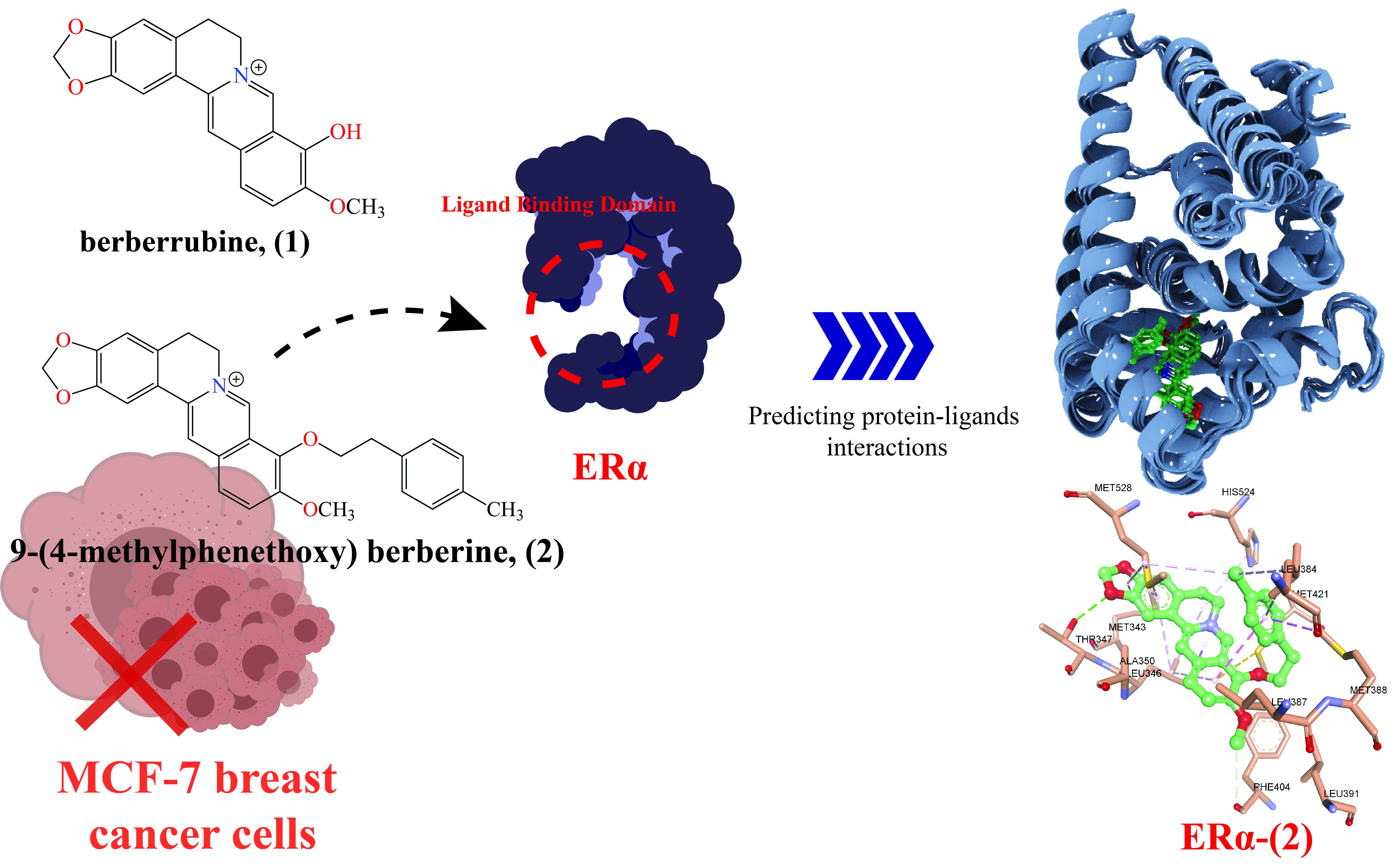
Breast cancer remains one of the most prevalent malignancies worldwide, with estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) playing a crucial role in its development and progression. In this study, we investigated the binding interactions and stability of berberrubine (1) and 9-(4-methyl phenethoxy) berberine (2) as potential ERα inhibitors using computational approaches. Molecular docking was performed to evaluate binding affinities and interactions, followed by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to assess the stability and conformational changes of the ERα-ligand complexes. The binding free energy was further analyzed using Molecular Mechanics/Generalized Born Surface Area (MM-GBSA) calculations to identify key energy contributions. The results demonstrated that (2) exhibited stronger and more stable binding to ERα than (1), though both were less potent than 4-hydroxytamoxifen (OHT), a standard ERα inhibitor. Additionally, ERα-(2) interacts with key residues ALA350, GLU353, and ARG394, while exhibiting stronger van der Waals interactions than ERα-(1), consistent with the MMGBSA energy component analysis. The study provides insights into the molecular mechanisms of ERα inhibition by berberine derivatives and highlights their potential as lead compounds for further development in breast cancer therapy.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2025-03-19
How to Cite
Ngueanngam, N., Jityuti, B., Patnin, S., Makarasen, A. ., Chotiwit, S. ., Samosorn, S. ., & Boonsri, P. (2025). In Silico Investigation of Estrogen Receptor Alpha Inhibition by Alkyleneoxyberberine Derivatives. Science Essence Journal, 41(1), 51–64. Retrieved from https://ejournals.swu.ac.th/index.php/sej/article/view/16638
Issue
Section
Research Article







