Nitrate Removal Enhancement Using Pulse Electrolysis and Aluminum Electrode
Keywords:
Nitrate in water sources, Nitrate removal method, Pulsed DC electrolysisAbstract
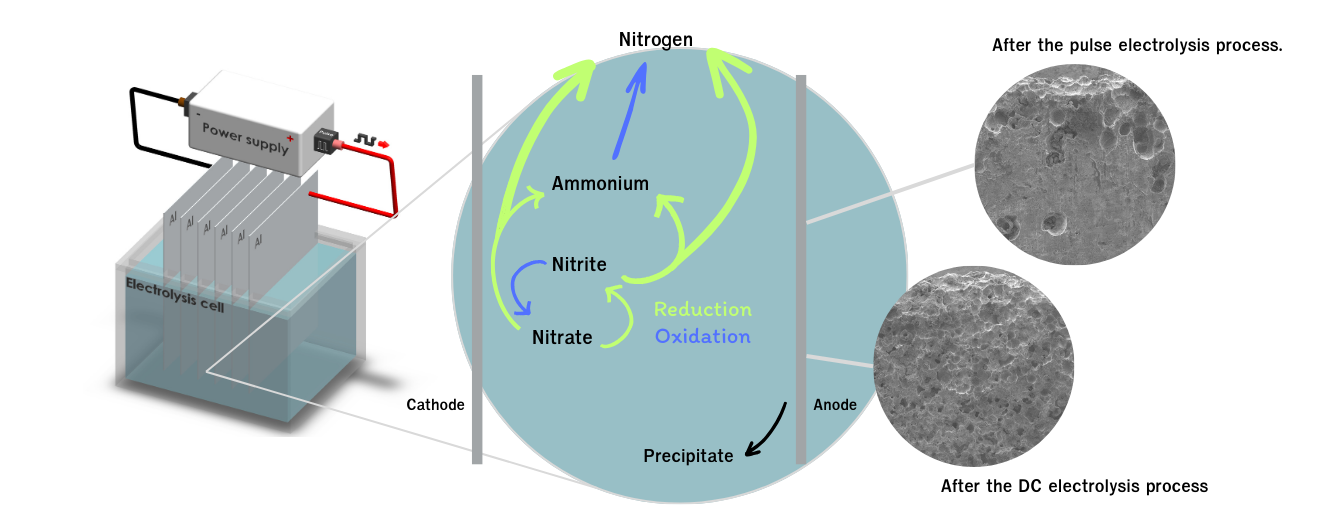
This work focuses on nitrate elimination from municipal wastewater by an electrochemical method with pulsed DC electrolysis. The performance of electroreduction of nitrate was investigated without alkaline electrolyte addition. The nitrate removal reactor was fabricated from acrylic and aluminum electrodes. The nitrate concentration was analyzed by the light absorption of the substance using UV-Vis spectroscopy. The precipitated compounds were determined by X-ray diffraction technique. The experimental results with 180 min treatment indicated the optimum condition for nitrate removal, which was carried out on the pulse frequency of 10 kHz, pulse width of 80%, and electric current density of 16 mA/cm2. This condition was able to eradicate nitrate up to 90.73% (4.3 mg/L) from an initial nitrate concentration of 46.0 mg/L with a nitrogen selectivity of 80.08%. Furthermore, the weight loss of aluminum anodes was as low as 0.8%. The main precipitation formed in the electrolyte cell was aluminum hydroxide.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2025-03-19
How to Cite
Suwannimit, P., Sakulkalavek, A., Klongratog, B. ., Somdock, N. ., & Srirach, P. (2025). Nitrate Removal Enhancement Using Pulse Electrolysis and Aluminum Electrode. Science Essence Journal, 41(1), 24–38. Retrieved from https://ejournals.swu.ac.th/index.php/sej/article/view/16633
Issue
Section
Research Article







