Vanillic Acid Suppresses Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Gastrointestinal Cancer Cells via Inhibition of mTOR Expression
Keywords:
Gastrointestinal cancer, Vanillic acid, Apoptosis, mTORAbstract
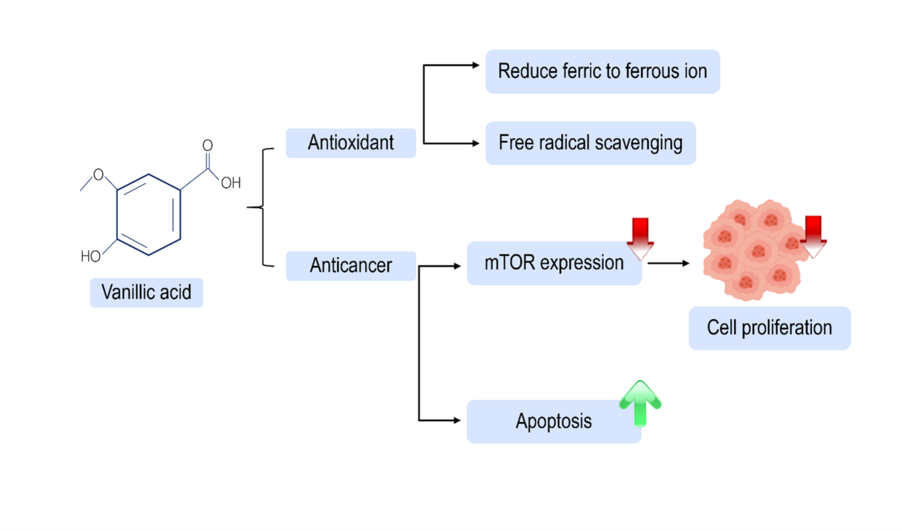
Gastrointestinal cancer is a major global health concern associated with high mortality rates. Adjuvant therapies, including surgery and chemotherapy, are widely used in cancer treatment. However, chemotherapy often causes significant side effects, harming healthy cells and leading to long-term complications. Therefore, alternative therapeutic strategies with fewer adverse effects are urgently needed. This study aimed to investigate the antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of vanillic acid, a phenolic compound on gastrointestinal cancer cell lines, specifically KKU-100 and HepG2 cell lines. The evaluation of antioxidant properties was conducted by the DPPH and FRAP assays, while cytotoxicity assessment was performed through MTT assays. The cell apoptosis rate was analyzed using flow cytometry, and the expression of the mTOR gene was quantified through real-time RT-PCR analysis. Our results demonstrated strong antioxidant activity, with a maximum FRAP value of 235.77±0.11 µgAAE/mg of vanillic acid and a DPPH free radical scavenging rate of 69.33±3.11%, with an effective concentration (EC50) of 2.69 mg/mL. Furthermore, vanillic acid significantly suppressed the proliferation of KKU-100 and HepG2 cell lines, with IC50 values of 1508 µg/mL and 634.3 µg/mL, respectively, in a dose-dependent manner. Flow cytometry analysis revealed a slight increase in apoptosis in both cell lines. Notably, vanillic acid downregulated mTOR expression in both KKU-100 and HepG2 cells. The findings suggested that vanillic acid, may serve as a promising therapeutic candidate for the treatment of gastrointestinal cancers.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2025-03-19
How to Cite
Pornphiphat, S., Janthamala, S. ., Siriprayong, A., Duenngai, K. ., Wongwattanakul, M. ., Thanee, M. ., Pinlaor, P. ., & Techasen, A. . (2025). Vanillic Acid Suppresses Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Gastrointestinal Cancer Cells via Inhibition of mTOR Expression. Science Essence Journal, 41(1), 39–50. Retrieved from https://ejournals.swu.ac.th/index.php/sej/article/view/16599
Issue
Section
Research Article







