SCOBY-Fermented Citrus x aurantium L. Peel with Enhanced Antioxidant and Cholesterol-Lowering Effects
Keywords:
Citrus x aurantium L., SCOBY fermentation, Phenolic content, Antioxidant, AntihypercholesterolemicAbstract
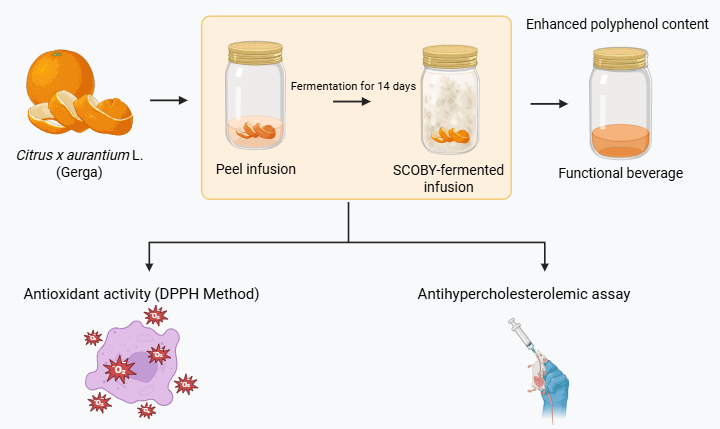
Citrus peels are rich sources of phenolic and flavonoid compounds with antioxidant and lipid-lowering effects, yet the bioactive profile of Citrus x aurantium L. (Gerga), a local Indonesian cultivar, has not been thoroughly investigated. Fermentation with a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) offers a promising strategy to biotransform phytochemicals and enhance their functional potential. This study compared the total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), antioxidant activity, and antihypercholesterolemic effect of C. x aurantium peel infusion and its SCOBY-fermented product. TPC and TFC were quantified spectrophotometrically. Antioxidant activity was evaluated using the DPPH radical scavenging assay, and cholesterol-lowering efficacy was assessed in hypercholesterolemic mice. Data were analyzed using an independent t-test for total phenolic content (TPC) and total flavonoid content (TFC), while lipid-lowering efficacy was evaluated using one-way ANOVA. Fermentation significantly increased TPC (26.5±0.01 to 42.9±0.03 mg GAE/g) and TFC (20.9±0.05 to 32.7±0.03 mg QE/g) (p < 0.05). The SCOBY-fermented product also exhibited stronger antioxidant activity (IC₅₀ = 11.98 vs. 14.64 mg/mL) and a greater reduction in serum total cholesterol compared with C. x aurantium peel infusion (29.84±1.03% vs. 27.71±0.25%). These findings indicate that SCOBY fermentation enhances the phenolic and flavonoid content, antioxidant potential, and antihypercholesterolemic activity of C. x aurantium peel infusion. This bioprocessing approach may provide a sustainable strategy for developing functional beverages from citrus by-products.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2025-11-26
How to Cite
Efendi, M. R., Faradila, H., Nabila, P., Joevanda, S., Ramadhani, H. R., Herzadania, T., Sari, S. M., & Rusdi, M. S. (2025). SCOBY-Fermented Citrus x aurantium L. Peel with Enhanced Antioxidant and Cholesterol-Lowering Effects. Science Essence Journal, 42(1), 1–13. Retrieved from https://ejournals.swu.ac.th/index.php/sej/article/view/17145
Issue
Section
Research Article







