Biochar as a Sustainable Additive: Performance Evaluation in Stone Matrix Asphalt and Bituminous Concrete Mix Designs
Keywords:
Biochar, Sustainable pavement, Stone matrix asphalt, Bituminous concrete, Mechanical performance, Cost-benefit analysisAbstract
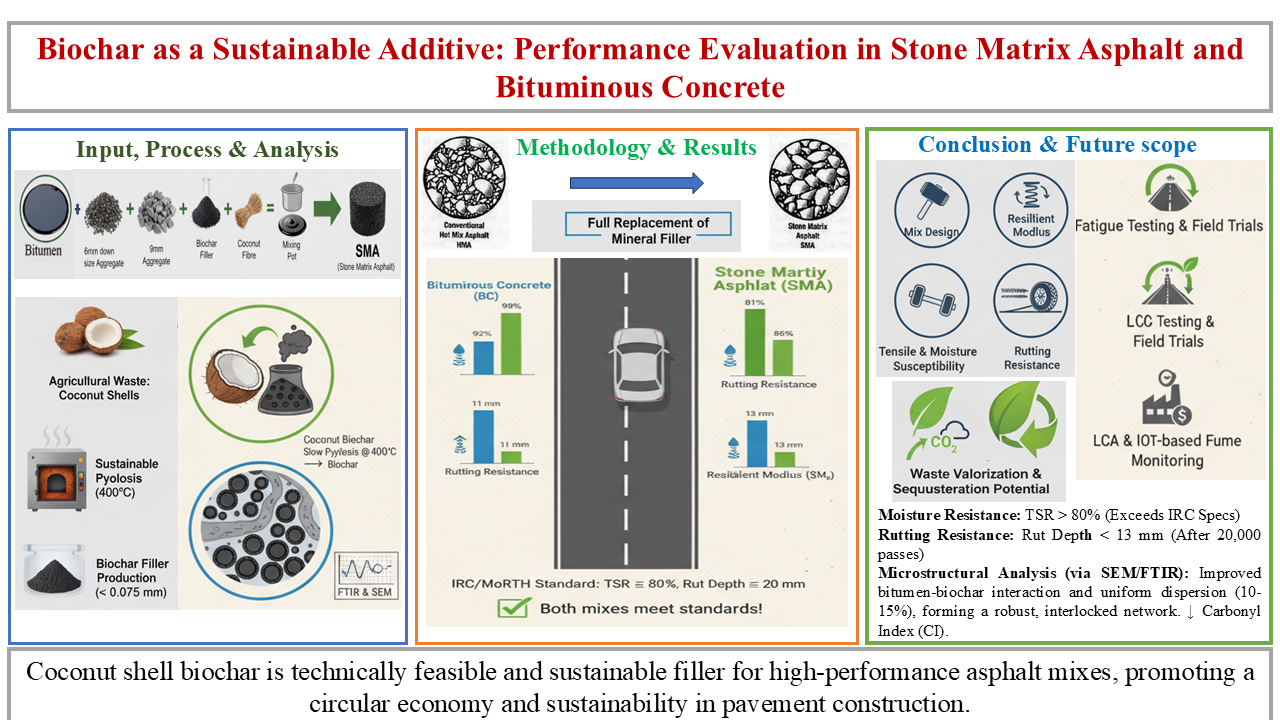
This study investigates coconut shell biochar as a full replacement for mineral filler in Stone Matrix Asphalt (SMA, 9%) and Bituminous Concrete (BC, 2%), designed in accordance with Indian Roads Congress and MoRTH standards. Performance was assessed using indirect tensile strength (ITS), Marshall stability, resilient modulus, rutting, and moisture susceptibility tests, with statistical analysis confirming the significance of observed variations. BC mixes retained tensile strength above 93% under freeze–thaw and 98% under humid conditioning, while SMA remained above the 80% threshold. Rut depths were within permissible limits for both mixes (11 mm for BC; 13 mm for SMA after 20,000 passes). Binder-level analyses (FTIR and SEM) confirmed improved bitumen–biochar interactions at 10–15% replacement, explaining the observed mechanical improvements and BC’s superior performance. Although stone dust provided marginally higher strength, biochar demonstrated strong technical feasibility along with added environmental benefits by valorising agricultural waste. Future studies should focus on fatigue testing, long-term field trials, and life-cycle assessment, where IoT-based bitumen fume monitoring can provide real-time emissions data to strengthen sustainability evaluations.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2026-01-19
How to Cite
Penki, R., Rout, S. K. ., & Das, A. K. (2026). Biochar as a Sustainable Additive: Performance Evaluation in Stone Matrix Asphalt and Bituminous Concrete Mix Designs. Science Essence Journal, 42(1), 96–112. Retrieved from https://ejournals.swu.ac.th/index.php/sej/article/view/17062
Issue
Section
Research Article







