Evaluation of Biological Activities and Cytotoxicity of Microporus vernicipes PW17-173 and Microporus xanthopus PP17-16 Mushroom Extracts for Natural Cosmetics Applications
Keywords:
Antioxidant, Anti-tyrosinase, Anti-inflammatory, Cytotoxicity, MushroomAbstract
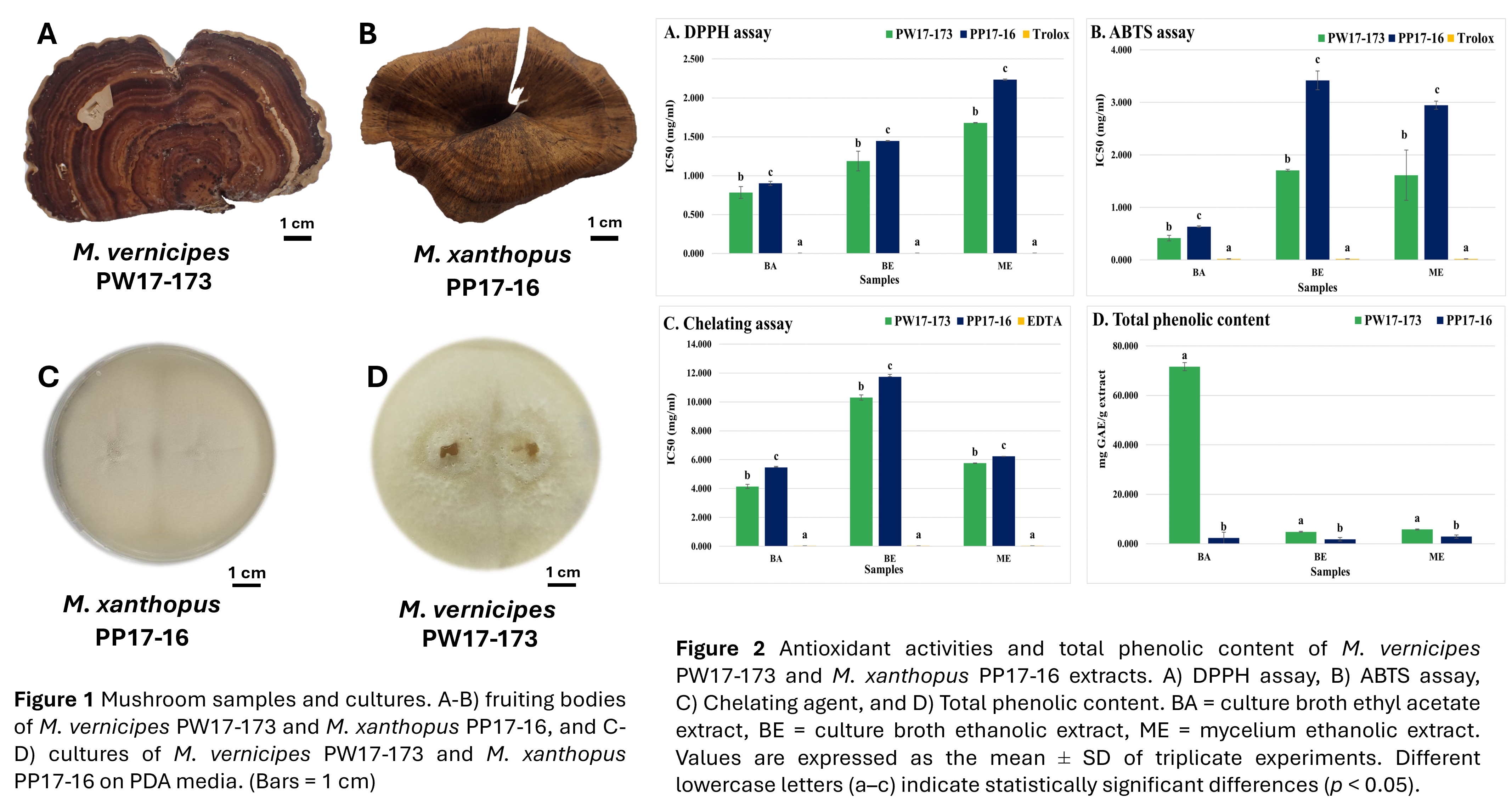
Mushroom extracts, known for their rich content of bioactive compounds such as polysaccharides, phenolic acids, vitamins, and minerals, are increasingly recognized for their potential as cosmeceuticals. This study evaluated Microporus vernicipes PW17-173 and Microporus xanthopus PP17-16, collected from northeastern Thailand. The mushrooms were cultured in yeast malt broth, and four extracts were prepared using ethanol and ethyl acetate: culture broth ethyl acetate (BA), culture broth ethanol (BE), mycelium ethyl acetate (MA), and mycelium ethanol (ME). These extracts were assessed for antioxidant, anti-tyrosinase, and anti-inflammatory activities. The BA extracts from both species exhibited the highest antioxidant activity, followed by the ME and BE extracts. Anti-tyrosinase assays revealed low IC50 values for BA extracts, with M. vernicipes showing 0.591±0.013 mg/mL and M. xanthopus 0.335±0.055 mg/mL. In anti-inflammatory tests, all extracts from M. vernicipes demonstrated lower IC50 values compared to those from M. xanthopus. Cytotoxicity assays on human keratinocyte (HaCaT) cells indicated that the BA and ME extracts caused 50% cell damage at concentrations above 250 µg/mL, while BE extracts exhibited similar toxicity at concentrations above 250 µg/mL for M. vernicipes and 63 µg/mL for M. xanthopus. These findings suggest that Microporus species offer promising potential for cosmetic formulations due to their potent antioxidant, anti-tyrosinase, and anti-inflammatory properties.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2024-12-28
How to Cite
Suwannasai, N., Karin, B., Nantavisai, K., Thamvithayakorn, P., Chotelersak, K., & Phosri, C. (2024). Evaluation of Biological Activities and Cytotoxicity of Microporus vernicipes PW17-173 and Microporus xanthopus PP17-16 Mushroom Extracts for Natural Cosmetics Applications. Science Essence Journal, 40(2), 58–73. Retrieved from https://ejournals.swu.ac.th/index.php/sej/article/view/16467
Issue
Section
Research Article







