การวิเคราะห์ความยั่งยืนของแม่น้ำเจ้าพระยาตอนล่างโดยใช้พลวัตระบบ
Main Article Content
Abstract
Rujira Chaysiri and Jitlakha Sukruay
รับบทความ: 13 เมษายน 2563; แก้ไขบทความ: 29 กันยายน 2563; ยอมรับตีพิมพ์: 26 ตุลาคม 2563; ตีพิมพ์ออนไลน์: 19 พฤษภาคม 2564
บทคัดย่อ
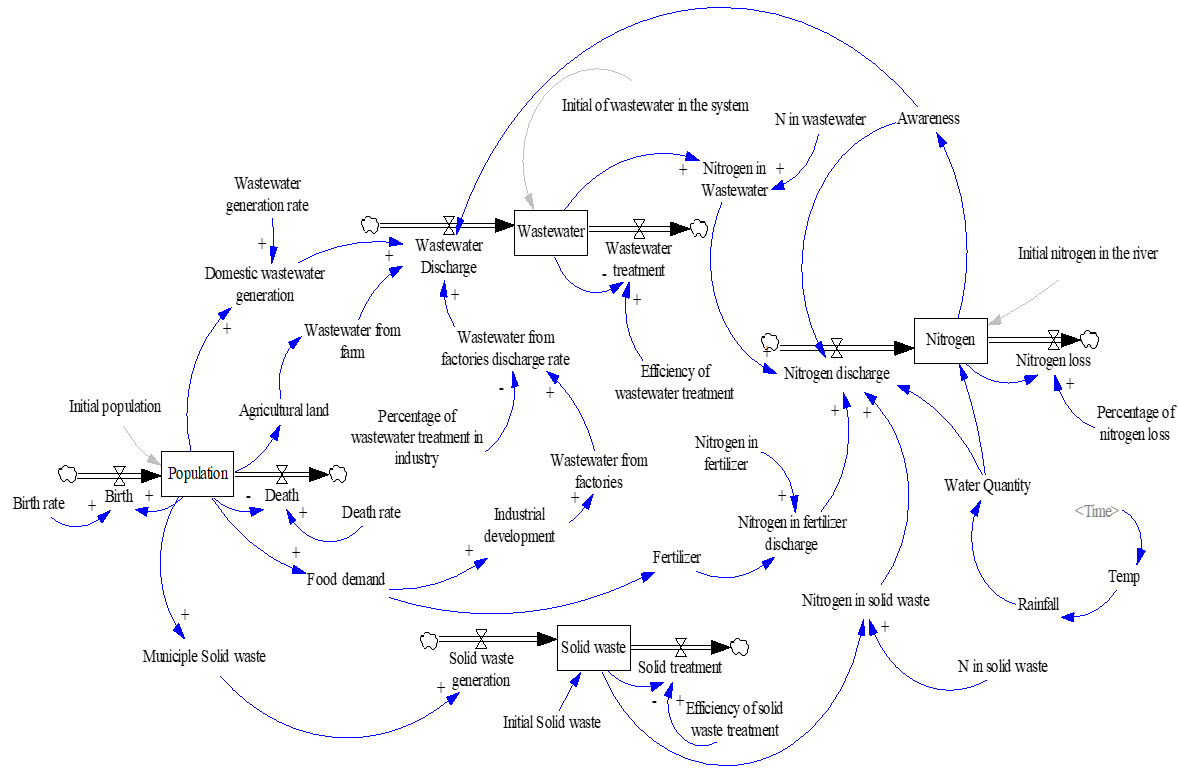
ปัญหาคุณภาพน้ำในแม่น้ำเจ้าพระยาได้รับการบันทึกไว้ในวรรณกรรมจำนวนมาก รวมถึงรัฐบาลได้ออกกฎและมาตรการต่าง ๆ เพื่อลดปัญหาสิ่งแวดล้อมในแม่น้ำ อย่างไรก็ตามปัญหาเหล่านี้ยังคงมีอยู่ ในงานวิจัยนี้คณะผู้วิจัยสร้างแบบจำลองพลวัตระบบที่เรียกว่า เจ้าพีเอสดี (ChaoPSD) ซึ่งเป็นแบบจำลองที่ประกอบไปด้วยสามระบบย่อย ได้แก่ ครัวเรือน อุตสาหกรรม และเกษตรกรรม แบบจำลองติดตามปริมาณไนโตรเจนของแม่น้ำเจ้าพระยาตอนล่างเมื่อเวลาผ่านไป หลังจากทดสอบแบบจำลองแล้ว แบบจำลองพลวัตระบบนำมาใช้เพื่อเป็นเครื่องมือสำหรับการเพิ่มความเข้าใจในความ สัมพันธ์ระหว่างพฤติกรรมของผู้ใช้แม่น้ำและสภาพคุณภาพน้ำในแม่น้ำ ผลของการจำลองแสดงให้เห็นว่ามีการเพิ่มขึ้นของปริมาณไนโตรเจนในแม่น้ำเจ้าพระยาตั้งแต่ปี 2561 ถึงปี 2566 คณะผู้วิจัยแนะนำว่าการควบคุมการปล่อยไนโตรเจนลงในน้ำซึ่งสามารถทำได้โดยการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพของการบำบัดน้ำเสียและการเพิ่มความตระหนักรู้ของผู้ใช้แม่น้ำ มีส่วนสำคัญต่อความยั่งยืนทางสิ่งแวดล้อมของแม่น้ำเจ้าพระยา
คำสำคัญ: พลวัตระบบ มลภาวะทางน้ำ แม่น้ำเจ้าพระยา ไนโตรเจน การจัดการน้ำ
Abstract
Water quality issues in the Chao Phraya river have been well–documented in the literature. The government has enforced rules and regulations to mitigate the environmental problems in the river. However, problems still exist. In this research, we constructed a system dynamics (SD) model, called ChaoPSD. The proposed model included three subsystems: (1) household, (2) industry, and (3) agriculture. This model tracked the nitrogen load in the lower Chao Phraya river over time. After the model validation, ChaoPSD was used as a tool for a better comprehension of the interrelationships among the actions of users and the health of the river. The simulation results showed that there will be an increasing amount of nitrogen in the Chao Phraya river from 2018 to 2023. We suggest that controlling the discharged nitrogen by increasing the efficiency of wastewater treatment and increasing people’s awareness are essential for environmental sustainability in the Chao Phraya river.
Keywords: System dynamics, Water pollution, Chao Phraya river, Nitrogen, Water management
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
Begum, M., and D'Haese, L. (2010). Supply and demand situations for major crops and food items in Bangladesh. Journal of the Bangladesh Agricultural Univer-sity 8(1): 91–102.
Borshchev, A., and Filippov, A. (2004). From system dynamics and discrete event to practical agent based modeling: reasons, techniques, tools. Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference of the System Dynamics Society. Oxford, England.
Boonta, A., Khanom, T., and Kodwong, W. (2010). Total Nitrogen Content. Retrieved from http://samkon-eve.blogspot.com/2010/ 07/7-total-nitrogen-content.html, January 3, 2020.
Bruning–Fann, C. S., and Kaneene, J. (1993). The effects of nitrate, nitrite and N–nitroso compounds on human health: A review. Veterinary and Human Toxicology 35(6): 521–538.
Chen, J., He, D., Zhang, N., and Cui, S. (2004). Characteristics of and human influences on nitrogen contamination in Yellow River system, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 93(1): 125–138.
Convention on Biological Diversity. (2010). Global biodiversity outlook 3.The Montréal, Canada: Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity. Retrieved from http://gbo3.cbd.int/, January 21, 2020.
Cooley, H., Ajami, N., Ha, M.–L., Srinivasan, V., Morrison, J., Donnelly, K., and Christian–Smith, J. (2014). Global water governance in the twenty–first century. The World’s Water (pp. 1–18). Springer.
Department of Local Administration [DLA]. (2015). The Volume of Wastewater and the Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment in Each Region, Thailand 2015. Ministry of Social Development and Human Security Retrieved from https://www.msoci ety.go.th/ewt_news.php?nid=18962, January 15, 2020.
Department of Local Administration [DLA]. (2015). The Volume of Wastewater and the Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment in Each Region, Thailand 2015. Ministry of Social Development and Human Security Retrieved from https://www.msociety.go.th/ewt_news.php?nid=18962, December 25, 2019.
Department of industrial works. (2008). List of Factories which Tend to Release Water Pollution. Chemical and Heavy Metal. Retrieved from http://www.diw.go.Th/hawk/content.php?mode=laws&tabid=1&secid=3&subid=0, January 4, 2020.
Figueredo, G. P., and Aickelin, U. (2011). Comparing system dynamics and agent–based simulation for tumour growth and its interactions with effector cells. Proceedings of the 2011 Summer Computer Simulation Conference (pp. 15–22). England: Cornell University.
Kathong, S., and Ruangviriyachai, D. C. (2014). Determination of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in liquid organic fertilizer. KKU Research Journal (Graduate Studies) 14(4): 57–68.
Kato, T. (2005). Simulation of water quality with the application of system dynamics model for population and land–use changes. Paddy and Water Environment 3(2): 103–109.
Khanh, D., and Thanh, N. H. (2010). Management of Agricultural Waste and Potential for Cobenefits. Retrieved from https://www.iges.or.jp/en/archive/wmr/pdf/activity100728/15_Khanh_Day1_Session5.pdf, January 13, 2020.
Koch, H., and Vögele, S. (2009). Dynamic modelling of water demand, water availability and adaptation strategies for power plants to global change. Ecological Economics 68(7): 2031–2039.
Macal, C. M. (2010). To agent–based simulation from system dynamics. Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference (pp. 371–382).
Martis, M. S. (2006). Validation of simulation based models: A theoretical outlook. The Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods 4(1): 39–46.
Ministry of Science and Technology. (2012). Fundamental Information of the Chao Phraya Basin. Hydro and Agro Informatics Institute (HAII) Retrieved from http://www. knowledge/128-hydro-and-weather/663-25basinreports.html, December 2, 2019.
Mirchi, A., Madani, K., Watkins, D., and Ahmad, S. (2012). Synthesis of system dynamics tools for holistic conceptualization of water resources problems Water Resource Management 26(9): 2421–2442.
Morales–Suarez–Varela, M. M., Llopis–Gon-zalez, A., and Tejerizo–Perez, M. L. (1995). Impact of nitrates in drinking water on cancer mortality in Valencia, Spain. European Journal of Epidemiology 11(1): 15–21.
National Statistic Office [NSO]. (2017). Population Distribution. Retrieved from http:// statbbi.nso.go.th/staticreport/page/sector/en/01.aspx, December 12, 2019.
Official Statistics Registration Systems. (2016). Demographic distribution in Thailand. Retrieved from http://stat.dopa.go.th/stat/statnew/upstat_age_disp.php, January 9, 2020.
Pollution Control Department [PCD]. (2014). Solid waste situation in Thailand from 2016. Retrieved from: http http://slbkb.psu.ac.th/jspui/handle/2558/1300, December 10, 2019.
Pollution Control Department [PCD]. (2017). Agricultural Wastewater Problem. Retrieved from http://www.pcd.go.th/info_serv/water_Agricultural.htm, January 3, 2020.
Pereira, H. M., Leadley, P. W., Proença, V., Alkemade, R., Scharlemann, J. P., Fernandez–Manjarrés, J. F., and Cheung, W. W. (2010). Scenarios for global biodiversity in the 21st century. Science 330(6010): 1496–1501.
Pluchinotta, I., Pagano, A., Giordano, R., and Tsoukiàs, A. (2018). A system dynamics model for supporting decision–makers in irrigation water management. Journal of Environmental Management 223: 815–824.
Pollution Control Department [PCD]. (2017). The Chao Phraya river situation. Retrieved from: http://www.pcd.go.th/info_serv/water_Chaopraya50.html#s15, January 15, 2020.
Royal Irrigation Department [RID]. (2017). Water Quantity in Rivers of Thailand [Data file]. Bangkok: Author.
Smith, V. H., Tilman, G. D., and Nekola, J. C. (1999). Eutrophication: impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environmental Pollution 100(1–3): 179–196.
Sterman, J. D. (1984). Appropriate summary statistics for evaluating the historical fit of system dynamics models. Dynamica 10(2): 51–66.
Sukholthaman, P., and Sharp, A. (2016). A system dynamics model to evaluate effects of source separation of municipal solid waste management: A case of Bangkok, Thailand. Waste Management 52: 50–61.
Sukruay, J., and Chaysiri, R. (2018). System dynamics model for estimating water pollution. International Scientific Journal of Engineering and Technology (ISJET) 2(2): 45–52.
Sumari, S., Ibrahim, R., Zakaria, N. H., and Ab Hamid, A. H. (2013). Comparing three simulation models using taxonomy: System dynamic simulation, discrete event simulation and agent based simulation. International Journal of Management Excellence 1(3): 54–59.
The World Bank. (2017). Thailand: Share of industry. Retrieved from http://www.theglo baleconomy.com/Thailand/Share_of_industry/, November 12, 2019.
Thitanuwat, B., Polprasert, C., and Englande, A. J. (2016). Quantification of phosphorus flows throughout the consumption system of Bangkok Metropolis, Thailand. Science of the Total Environment 542(Part B): 1106–1116.
Towprayoon, S. (2007). Wastewater Flow and Solid Waste Stream in Thailand. Retrieved from http://www-gio.nies.go.jp/wgia/ wg4/pdf/20_II_05_Waste_Towprayoon_Thailand.pdf, December 23, 2019.
UN–Water. (2016). Towards a Worldwide As-sessment of Freshwater Quality. Retrieved from http://www.unwater.org/pub lications/towards-worldwide-assessment-fresh water-quality/, January 14, 2020.
UNESCO. (2018). The Global Water Quality Challenge & SDGs. Retrieved from https:// en.unesco.org/waterquality-iiwq/wq-challenge, January 14, 2020.
Venkatesan, A. K., Ahmad, S., Johnson, W., and Batista, J. R. (2011). Systems dynamic model to forecast salinity load to the Colorado River due to urbanization within the Las Vegas Valley. Science of the Total Environment 409(13): 2616–2625.
Wang, Q. S., Sun, D. B., Hao, W. P., Li, Y. Z., Mei, X. R., and Zhang, Y. Q. (2012). Human activities and nitrogen in waters. Acta Ecologica Sinica 32(4): 174–179.
Water Quality Management Office. (2017). Domestic Wastewater. Pollution Control Department Retrieved from http://www.pcd.go.th/info_serv/water_wt.html#s1, Decomber 19, 2019.
Yukalang, N., Clarke, B. D., and Ross, K. E. (2017). Solid waste management in Thai-land: An overview and case study (Tha Khon Yang sub–district). Reviews on Environmental Health 32(3): 223–234.